
Why is choosing the right abrasive media for the job so important?crush
If you use a mismatched abrasive for a blasting job, you may end up having to redo the job, because the anchor pattern is incorrect, or cause unwanted damage to the blasted surface.
There are several types of abrasive blasting applications: cleaning, finishing, and surface prep for coatings, to name a few. By using the appropriate type of abrasive media, along with the right type of delivery, wet or dry blast, direct pressure or siphon blast, you will set yourself up for a successful, profitable blasting job.
Table of Contents
- Surface Prep
- Mohs Hardness
- Density and Specific Gravity
- Particle Shape
- Anchor Pattern
- Mesh Size
- Number of Recycles
- Bonus: Comparative Chart of Factors
Blasting for Surface Preparation and Finishing
Selecting the right abrasive media for surface prep is vital. This is because different media types have different characteristics, and create different surface profiles.
The anchor pattern that an abrasive creates will determine how effectively a coating bonds to a prepared surface.
What type of anchor pattern you need to create to apply a coating depends on the surface being treated.
Factors to Consider When Selecting An Abrasive
Some of the things you should consider when choosing an abrasive are hardness, density, shape of the abrasive, the type of profile the abrasive will leave, friability, how many times you can recycle the abrasive, and overall cost.
Mohs Hardness
One of the things abrasives are measured by is the Mohs Hardness Scale. This hardness scale was created by German mineralogist and geologist Freidrich Mohs.
How the scale works is the lower the number, the softer the mineral. The higher the number, the harder the mineral. Talc is a 1, diamond is a 10. Higher number materials can scratch or etch lower number materials.
Here’s the Mohs hardness for several popular abrasives.
| Abrasive | Mohs Hardness |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | 9 |
| Crushed Glass | 5 to 6 |
| Glass Beads | 5 to 6 |
| Garnet | 7.5 to 8.5 |
| Silicon Carbide | 9 to 9.5 |
| Nickel Slag | 7 |
| Copper Slag | 7 |
| Steel Shot | 8 |
| Steel Grit | 8 |
| Plastic Abrasive | 3 to 4 |
| Staurolite | 7 to 7.5 |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | 2.5 |
| Walnut Shell | 4 to 5 |
| Corn Cob | 4 to 4.5 |
The softer the abrasive, the finer the finish will be. Harder abrasives are useful for removing certain types of corrosion and rust. Softer abrasives are best for cleaning up grease, grime, and removing light coatings. Softer abrasives are preferred when you do not want to leave an anchor pattern in the substrate.
Also, the more pressure you blast with, the velocity and force the abrasive will be thrown with. You can always adjust the blasting pressure, but you cannot change the characteristics of the abrasive itself. For that reason, it is important to look at the shape, as well as the hardness of an abrasive.
Density Plays a Role in Abrasive Blasting
Blasting abrasives each a different density. In simplest terms, the more dense a molecule is, the tighter the atoms are packed together. The denser the substance, the more kinetic energy it can hold.
The denser the particle, the more impact it has over a smaller area, meaning a deeper surface profile. Less dense particles create a less deep profile, since they hit with less force. (Speed + mass = force of impact).
Density is measured in specific gravity, with water being a 1.0 SG. The more dense a substance is, the higher specific gravity it will have.
| Abrasive | Density (Specific Gravity) |
|---|---|
| Walnut Shell | 1.2 to 1.35 |
| Corn Cob | 1.2 to 1.4 |
| Plastic Abrasive | 1.5 |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | 2.2 |
| Glass Beads | 2.5 |
| Crushed Glass | 2.5 |
| Copper Slag | 2.8 to 3.6 |
| Nickel Slag | 2.8 to 3.8 |
| Silicon Carbide | 3.2 to 3.22 |
| Staurolite | 3.6 |
| Garnet | 3.5 to 4.3 |
| Aluminum Oxide | 3.94 to 3.96 |
| Steel Shot | 4.8 to 7.8 |
| Steel Grit | 4.8 to 7.8 |
How The Shape of an Abrasive Affects the Surface Profile
There are four basic shapes in abrasives: angular, sub-angular, sub-rounded, and rounded.

Angular abrasives have many facets, and several jagged faces and vertices. Examples of angular abrasives are crushed glass and certain types of slag. Angular abrasives are good for stripping corrosion and rust.
Sub-angular abrasives have some jagged edges, but less than angular types. Some abrasives that fall in this category include garnet and plastic urea.
Sub-rounded abrasives are not quite smooth, and the jagged edges are almost gone. This type of abrasive include staurolite and walnut shells.
Rounded abrasives are smooth, or may even be spherical. Glass beads or steel shot would be examples of rounded abrasives. Usually, rounded abrasives are used for removing mill scale (from hot rolled steel) or thin factory coatings.
Types of Anchor Patterns and Surface Profiles
As the blast media hits the surface, it creates substrate profiles in the shape of the abrasive.
Rounded abrasives create a dimpled profile, like the surface of a golf ball. This is also known as peening.
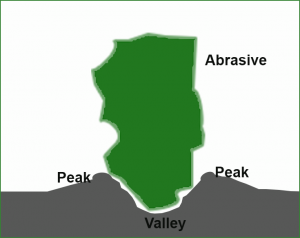
Angular and sub-angular abrasives create deeper, more pronounced anchor patterns. When the blasted abrasive hits the surface, two things happen: an indentation is made in the surface, and part of the surface is pushed up around the indentation. For every action, there is an opposite and equal reaction.
The indentations in the surface are known as valleys; the part of the surface pushed upwards are known as peaks. The distance between the top of the peak and bottom of the valley is known as a depth profile.
Each coating has a specific depth profile that must be achieved for optimal bonding. This is the surface roughness, or anchor pattern that best allows the coating to set. Ideally, the coating will cover the peaks and fill the valleys.
If the peaks are too high, they may push up through the coating, and rust will prematurely form. If the depth profile is not deep enough the coating may not adhere correctly, and prematurely erode. Ideally, your applied coating will cover the peaks and fill the valleys.
The size of the abrasive, as well the shape, has an effect on the resulting anchor profile.
Considering The Mesh Size of the Abrasive
Generally speaking, it is best to use the finest abrasive available that will create the necessary surface profile.
Abrasives are usually measured in grit size, microns, or mesh size.
Grit Size to Microns to Mesh
| Grit Size | Mesh USS | Microns (Avg) | Inches (Avg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #4 | 3.5 | 5600~4750 | 0.187 |
| #5 | 4 | 4750~4000 | 0.157 |
| #6 | 5 | 4000~3350 | 0.132 |
| #7 | 6 | 3350~2800 | 0.111 |
| #8 | 7 | 2210 | 0.087 |
| #10 | 8 | 1854 | 0.073 |
| #12 | 10 | 1600 | 0.063 |
| #14 | 12 | 1346 | 0.053 |
| #16 | 14 | 1092 | 0.043 |
| #20 | 16 | 940 | 0.037 |
| #24 | 20 | 686 | 0.027 |
| #30 | 25 | 559 | 0.022 |
| #36 | 30 | 483 | 0.019 |
| #46 | 40 | 356 | 0.014 |
| #54 | 45 | 305 | 0.012 |
| #60 | 50 | 254 | 0.010 |
| #70 | 60 | 203 | 0.008 |
| #80 | 70 | 165 | 0.0065 |
| #90 | 80 | 145 | 0.0057 |
| #100 | 100 | 122 | 0.0048 |
| #120 | 120 | 102 | 0.0040 |
| #150 | 140 | 89 | 0.0035 |
| #180 | 170 | 76 | 0.0030 |
| #220 | 200 | 63 | 0.0025 |
| #240 | 200 | 50-53.5 | 0.0020 |
You can also find a more complete grit size to microns to mesh to inches chart here.
Recycles and Total Cost
Some blasting abrasives, like aluminum oxide or silicon carbide, cost more up front, but are economical in the long run, because they can be recycled many times.
Other types of abrasive blast media, like crushed glass or metal slag, are primarily used for outdoor blasting, and meant to be used and cleaned up. These are usually cheaper than other blast media, but only good for a few recycles in a blast cabinet or blast room.
Some abrasives are in the mid-range of cost and recycles. Glass beads or plastic urea both fit this description.
Consider what types of abrasive blasting jobs you do most frequently, and what type of media you need to stock to be profitable and efficient.
| Abrasive Recycle Rate by Media Type | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrasive Type | Max Impact Pressure (Siphon) | Max Impact Pressure (Direct Pressure) | Cold Roll Steel Part Hardness | Recycle Uses Average | ||||||
| Glass Beads | 80 PSI | 40 PSI | B72 to B86 | 30 uses | ||||||
| Aluminum Oxide | 90 PSI | 45 PSI | B72 to B86 | 50 uses | ||||||
| Silicon Carbide | 80 PSI | 40 PSI | B72 to B86 | 70 to 100 uses | ||||||
| Steel Shot | 130 PSI | 100 PSI | B72 to B86 | 100 uses | ||||||
| Plastic Urea | 80 PSI | 40 PSI | N/A | 30 uses | ||||||
| Walnut Shells | 70 PSI | 35 PSI | N/A | 4 to 5 uses | ||||||
| Sodium Bicarbonate | 70 PSI | 40 PSI | N/A | Single Use | ||||||
| Slag | 50 PSI | 25 PSI | N/A | 2 to 3 uses | ||||||
| Garnet | 60 PSI | 30 PSI | N/A | 4 to 5 uses | ||||||
Abrasive Media Comparative Chart
There are many types of abrasives for many different types of blasting applications. This chart compares the most common abrasives for a variety of factors.
| Abrasive | Mohs Hardness | Density | Shape | Mesh Sizes | Friability | Recycles | Cost | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide | 9 | 3.94 to 3.96 | Angular / Sub Angular | 12 to 325 | Low to Med | 50 | $$$ | Mfg |
| Crushed Glass | 5 to 6 | 2.5 | Angular | 30 to 325 | Med | 1 to 3 | $ | Mfg |
| Glass Beads | 5 to 6 | 2.5 | Rounded | 30 to 325 | Med | 30 | $$$ | Mfg |
| Garnet | 7.5 to 8.5 | 3.5 to 4.3 | Sub Angular / Sub Round | 8 to 150 | Med | 4 to 5 | $$$ | Nat |
| Silicon Carbide | 9 to 9.5 | 3.2 to 3.22 | Angular | 8 to 325 | Low | 70 to 100 | $$$$ | Mfg |
| Nickel Slag | 7 | 2.8 to 3.8 | Angular | 12 to 80 | High | 2 to 3 | $ | B-P |
| Copper Slag | 7 | 2.8 to 3.6 | Angular | 12 to 80 | High | 2 to 3 | $ | B-P |
| Steel Shot | 8 | 4.8 to 7.8 | Rounded | 7 to 120 | High | 100+ | $$$ | Mfg |
| Steel Grit | 8 | 4.8 to 7.8 | Angular / Sub Angular | 10 to 200 | High | 100+ | $$$ | Mfg |
| Plastic Abrasive | 3 to 4 | 1.5 | Sub Angular | 12 to 80 | Med to High | 30 | $$$ | Mfg |
| Staurolite | 7 to 7.5 | 3.6 | Sub Rounded | 20 to 120 | Med | 2 to 3 | $$ | Nat |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | 2.5 | 2.2 | Sub Rounded | 70 to 220 | Very High | Single Use | $$ | Mfg |
| Walnut Shell | 4 to 5 | 1.2 to 1.35 | Sub Rounded / Sub Angular | 6 to 100 | Med-High | 4 to 5 | $$$ | B-P |
| Corn Cob | 4 to 4.5 | 1.2 to 1.4 | Sub Angular | 8 to 40 | Med-High | 4 to 5 | $$ | B-P |
If you have any questions, please contact us, and we’ll be happy to help you make the best choice for your needs.
